《Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (8th Edition)》第五章 “The Network Layer: Control Plane” 的学习笔记。
Introduction
control plane 需要计算出 forwarding table / flow table,有两种方式:
- per-router control: router 之间互相发送信息,分别进行计算
- logicially centralized control: 使用 remote controller 集中地获取信息、计算、分发结果
Routing Algorithms
在 routing algorithm 中,网络被抽象为一张图,考虑 physical length、link speed、monetary cost 等因素作为边权。
routing algorithm 可以分为:
- centralized / decentralized:计算过程中是否知道整个图的信息
- static / dynamic:是否对网络负载、拓扑结构等的改变即时做出响应
- load-sensitive/insensitive: 是否考虑 congestion 状况
The Link-State (LS) Routing Algorithm
LS 是一个 centralized routing algorithm,需要每个 node 将其 attached links 的信息进行广播(link-state broadcast),使得每个 node 都有整张图的信息,再用 Dijkstra 等算法计算最短路。
在 load-sensitive routing algorithm 中,traffic load 的改变可能导致 oscillation,要么改为 load-insensitive,要么设法保证各个 router 不同时运行 routing algorithm。
The Distance-Vector (DV) Routing Algorithm
每个 node 维护一个到其他每个 node 的 distance vector,告诉 neighbor 自己的 distance vector,通过 neighbor 的 distance vector 更新自己的 distance vector。link state 发生改变时,会经过多轮迭代进行传播并最终收敛。
在 link cost 减小时,收敛是较快的。
但是在 link cost 增大时,收敛可能需要边权值域大小轮次的迭代(称作 count-to-infinity problem),并在过程中产生 routing loop,例如下图所示的情况:1
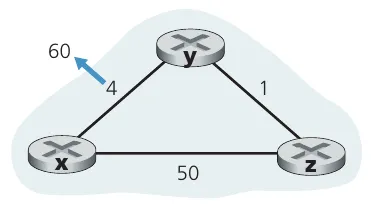
使用 poisoned reverse 可以避免出现二元环:如果 使用了 这条边来走向 ,则在 告诉 的 distance vector 中, 到 的距离是 。
但是 poisoned reverse 不能避免多元环的出现。
Comparison of LS and DV Routing Algorithms
- message complexity: LS 需要让每个 node 都获取到全局的 link state,要传送大量信息,且信息需要发送到很远的地方;DV 只需要从 neighbor 获取信息。
- speed of convergence: LS 有 Dijkstra 的低复杂度,DV 则较慢,而且过程中可能出现 routing loop,还有 count-to-infinity problem。
- robustness: 在 LS 中,每个 node 可以提供错误的 link state,但影响有限,每个 node 只为自己计算 forwarding table;在 DV 中,每个 node 的计算结果都是其他 node 的计算的一部分,影响可以很大。
实际上,Internet 同时使用了这两种算法。
Intra-AS Routing in the Internet: OSPF
如果统一管理所有 router,一方面规模过大性能无法接受,另一方面无法满足自治的需求。所以,实际上 router 被分成了很多个 autonomous system (AS),每个 AS 有一个 ICANN 赋予的编号。例如,每个 ISP 可能管理着一个或多个 AS。
每个 AS 内使用同一个 intra-AS routing protocol,例如 OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) ,它非常复杂,书中只有简要介绍。
OSPF 使用的是 LS routing algorithm,边权由管理员设置,每个 router 都会向整个 AS 内的其他所有 router(在 link state 发生变化时 & 周期性地)broadcast link state。
- OSPF message 直接通过 IP 传输,不使用 transport-layer protocol。
- 支持 authentication。
- 有多条最短路时,可以同时使用。
- 有 MOSPF 扩展来支持 multicast。
- 可以将 AS 划分为多个 area 形成 AS 内部的 hierarchy,每个 area 内部走最短路,不同 area 之间通过每个 area 的 border router 走 backbone area。
Routing Among the ISPs: BGP
The Role of BGP
BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) 是所有 AS 共用的 inter-AS routing protocol,将各个 AS 连接在一起。
在 BGP 中,destination 不是特定的 IP address,而是 CIDR prefix。BGP 使得一个 AS 可以向其他 AS advertise prefix,并计算出到达各个 prefix 的 route。
Advertising BGP Route Information
不同 router 之间会建立称作 BGP connection 的 TCP connection(不是 physical link),一般来说负责连接两个 AS 的 gateway router 之间会建立 external BGP (eBGP) connection;而 AS 内部的 router 两两之间建立 internal BGP (iBGP) connection。
一条 BGP advertisement(称作一个 route)包含 AS-PATH 和 NEXT-HOP 等信息:
- AS-PATH 即经过哪几个 AS 能到达目的地,一个 AS 收到来自其他 AS 的 route 后,可以在 AS-PATH 中加上自己,继续向 neighbor 发送;
- NEXT-HOP 是从当前 AS 出发向目的地走,走出当前 AS 遇到的第一个 router 的 IP address。
Determining the Best Routes
从一个 AS 出发到达某个 prefix 可能有很多条路径,BGP 按照下面的顺序来决定 best route(平局则使用下一条规则):
- 由管理员设置或从其他 AS 获取的 local preference
- shortest AS-PATH(经过最少个 AS)
- 在 AS 内走最短路(通过 intra-AS protocol 以及 NEXT-HOP 得到)到达 gateway router
- 根据 BGP identifier 选
IP-anycast
BGP 可以计算出到达某个 prefix (IP address) 的 best route,如果为多个 host 设置相同的 IP address,则可以实现 IP-anycast,例如在 CDN 中可以让用户从多个内容相同的 server 中挑选最适合的一个,而这一挑选是在 router 处通过 BGP 实现的。
但是 IP-anycast 如果用于 TCP 可能导致同一个 TCP connection 发给不同 host,所以 CDN 一般不采用 IP-anycast,而 DNS root server 则采用了 IP-anycast(DNS 使用 UDP)。
Routing Policy
BGP 通过 local preference 给管理员提供了决定如何选择 route 的自由,以实现某些 policy。
例如,当一个 access ISP 连接到多个 backbone ISP(即 multi-home)时,access ISP 不应该作为中介在不同 backbone ISP 之间进行传输。一般来说,一个 ISP 只会在通信双方至少有一方是其 customer 时提供服务。
The SDN Control Plane
SDN 分为 SDN controller、network management applications(例如 routing、access control、load balancing)、controlled devices 三个部分。其中 SDN controller 连接了 network management applications 和 controlled devices。
SDN 使用 generalized forwarding,将 data plane 和 control plane 分开,通过 network management applications 提供 network control functions,实现了 programmable network。
SDN 将 network functionality 进行了 unbundle,使得 packet switches、SDN controller、network management applications 可以来自不同的供应商,各自发展。
- communication layer (northbound API): controlled devices 和 SDN controller 进行通信。SDN controller 向 controlled device 发送信息(例如 flow table),从 controlled device 获取 link state 等信息,并在 network state 发生改变时被通知。可以使用 OpenFlow、SNMP 等协议。
- network-wide state-management layer: SDN controller 存储了一些信息,包括 network state、flow table、统计数据等。
- interface to the network-control application layer (southbound API): network management applications 可以从 SDN controller 获取 network state,订阅状态发生改变的 event。通过 RESTful API 等方式通信。
在 OpenFlow 中,SDN controller 可以向 controlled device 发送:
- configuration,修改配置参数
- modify-state,例如修改 flow table
- read-state,例如获取统计信息
- send-packet,让 router 发出一个 packet
controlled device 可以向 SDN controller 发送:
- flow-removed: 通知一个 flow table entry 已被移除(timeout 或者被 modify-state 删除)
- port-status: 例如一个 link up/down 了
- packet-in: 如果一个 packet 在 flow table 中没有 match,或者 action 为发送到 controller
ICMP: The Internet Control Message Protocol
ICMP 用来进行 router 和 host 之间的通信,作为 IP payload 进行传输。
ICMP message 有很多种,例如:
- 用来 ping 的 echo request 和 echo reply
- destination network/host/protocol/port unreachable
- router advertisement
- router discovery
- TTL expired
- IP header bad
Traceroute 就是通过 ICMP 实现的:向一个 unlikely port number 发送 TTL 递增的 UDP datagram,通过 TTL expired 得到每个 router 的信息,通过 port unreachable 得到终点的信息。
Network Management and SNMP, NETCONF/YANG
Network management involves the deployment, integration and coordination of all the hardware, software and human elements to monitor, test, poll, configure, analyze, evaluate, and control the network and element resources to meet the real-time, operational performance and quality-of-service (QoS) requirements at reasonable cost.2
network management 包括 managing server (以及 network manager)、managed device、data(每个 device 有 configuration、operational data、device statistics,而 managing server 有每个 device 以及整个 network 的 data)、network management agent、network management protocol。
network management 有若干方式:
- CLI: error-prone,难以 scale。
- SNMP/MIB: 每个 device 有 management information base (MIB) objects,可以通过 simple network management protocol (SNMP) 来获取/设置 MIB objects 中的 data,device 也可以通过 trap message 向 managing server 通知状态变化。SNMP/MIB 是针对单个 device 的,也难以 scale。
- NETCONF/YANG: NETCONF 比起 SNMP 更注重于配置管理,可以一次性操控多个 device (atomic network management transaction),可以设置 constraint 检查配置的正确性,使用 YANG 作为 data modeling language,以 XML 格式通过 TLS 进行通信。
Footnotes
-
p393, Figure 5.7: Changes in link cost, b. ↩
-
Saydam, T., Magedanz, T. From networks and network management into service and service management. J Netw Syst Manage 4, 345–348 (1996). https
:// ↩doi . org / 10 . 1007 / BF02283158